Here I will tell you everything you need to know about visiting some of the most disregarded biomes in existence: freshwater lakes/ponds. Every lake or pond is different, so I will give a general overview of what you can expect at any, as well as some of the highlights in some specific places.
Abiotic Features
- The sun- A lake in Alaska will receive much different amounts of light than a lake in Ecuador. The Sun gives energy to algae and other plants to carry out photosynthesis. This is the start of the food web.
- Oxygen levels- The higher in elevation you go, the less oxygen is in the air. This can affect the rate of growth for different species of plants as well as what species of fish are able to live there.
- Temperature-Again, it is regulated by the location of the lake as well as the surrounding natural features. A lake in the desert will be hit with much more sunlight than one surrounded by trees or mountains. Also, temperatures tend to vary based on elevation and latitude.
Biotic Features
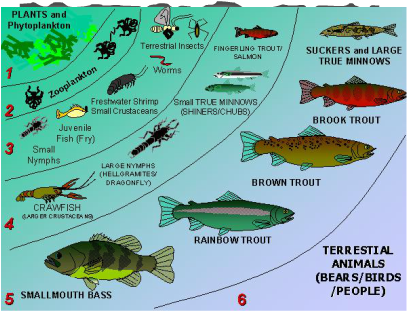
- Producers-These can include a wide variety of plants from algae to Water Lily's to different species of reeds. All depends on what works for that specific location. These plants all serve many purposes with the primary ones being to provide a food source and shelter for the consumers. This level of the food pyramid uses the highest amount of energy and has the highest population.

 Sharon Barrotz
Sharon Barrotz
- Consumers-Again, each location throughout the globe has its own region specific species which inhabit its waters. These can range from small bait fish including different varieties of shad, all the way up to alligators or bald eagles, and everything in between.
 Josh Velocity
Josh Velocity Phil Degginger
Phil Degginger
- Decomposers-Fungi and bacteria exist in many different lakes. The role of both is primarily to break down organic material such as wood, leaves, algae, etc. All species of freshwater decomposers are microscopic.

- Humans-Of course, humans love recreation, especially at lakes. Almost any human contact at a lake can change something in the biome. What I am mainly talking about is pollution. Trash, oil from motors and fishing line are all types of pollutants that can damage an ecosystem. Some other causes which don't actually take place at the lake are sewer or farm runoff. These can start a process called eutrophication, which begins with a spike in organic material such as phosphates or nitrates. These cause there to be rapid growth of algae, which eventually dies and is decomposed by bacteria. The bacteria absorb all the oxygen in the area thus creating a dead zone.

Evolutionary Adaptations
- Animals- Many animals have a symbiotic relationship with a type of plant. One example is a water lily and a frog. The frog uses the lily pad as a place to hide as well as a food source. Other types of plants help fish with the same types of things (i.e. shelter, etc.).
- Plants-Plants such as the Water Lily have special floating pads on the surface of the water to be able to absorb enough sunlight for photosynthesis.
No comments:
Post a Comment